While many tend to overlook this mechanical device, they are common to vehicles with manual transmissions. Car flywheels are an important mechanical device capable of storing rotational kinetic energy. They then release the preserved energy when the car requires them, maintaining a steady torque output.
Although not often talked about, the flywheel in car engines improves the driving experience. This article will discuss flywheel functions, its types, and other important information about the car flywheels.What is a Flywheel in Your Car?
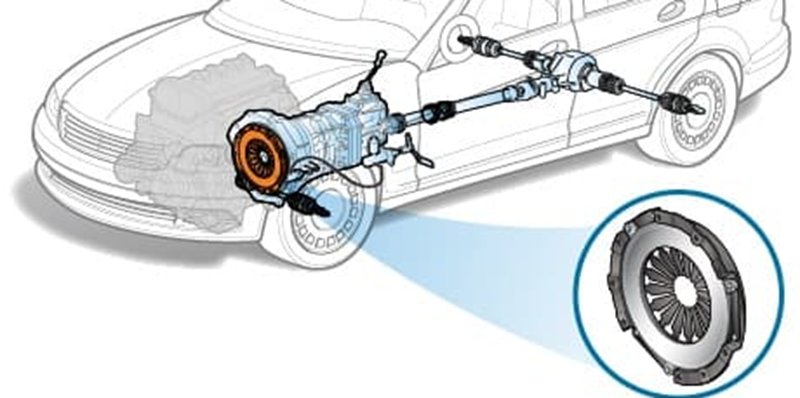
A flywheel is a circular structure connecting the car’s engine output shaft. It’s a mechanical device, presented as a wheel having a disc-like shape. The flywheel is important in the clutch transmission system of an automobile. It aids in storing rotational kinetic energy for various applications, particularly for delivering it to the vehicle’s transmission to promote the smooth running of the car.
The flywheel in car engines usually consists of a heavy cast iron. The primary function of the car wheel is to ensure stable and consistent rotational motion of the transmission system, preventing uneven speed. In addition, this device is usually at the rear end of the engine’s crankshaft, connecting to a rod, allowing it to drive the engine shaft rotation and maintain uniform torque output.
 Functions of Car Flywheels
Functions of Car Flywheels
We already explained how important the flywheels are to the total function of your vehicle. Below, we will discuss flywheel functions and roles in detail.
Engine Balancing
One of the main purposes of flywheels is to provide balance to the engine. When driving, the crankshaft rotates, generating vibrations and forces around the pistons and other moveable engine parts. In addition, the weighty flywheel disc reduces the vibrational effects and the imbalances that the combustion cycle creates. This results in a more stable engine operation and seamless driving.
Energy Storage and Optimization
The automobile flywheel also acts as an energy storage system, allowing better utilization. During car driving, there may be fluctuation in engine efficiency. During excesses, the flywheel device accumulates rotational energy, storing it as kinetic energy. However, when there’s a drop in energy, such as during the non-power phases of the engine cycle, it distributes it, making power available.
Clutch Functionality
Generally, the flywheel in car engines closely relates to the clutch system. However, this particular role is more pronounced in vehicles with manual transmission. The flywheel assists in limiting the effects of friction. It aids in smoothening the engaging and disengaging of power between the car’s transmission system and the engine, enabling gear changing and overall vehicle functionality.
Reduced Speed Fluctuations
The combustion cycle is an essential mechanism during driving, required for powering the automobile. However, during this cycle, power generation is not uniform, which ought to result in speed variations. Here’s where the flywheel comes into play. Its rotational inertia acts as a stabilizer, absorbing, evening, and minimizing these fluctuations in the transmission. Therefore, there is a significant drop in the chances of speed fluctuations. Instead, the vehicle maintains a steady speed, improving comfort and the overall driving experience.
Enhanced Crankshaft Rotation
Another essential function of the transmission flywheel is maintaining the rotational movement of the crankshaft. During each power stroke, energy is transferred to the flywheel, which stores and releases energy subsequently during the non-power stroke phase. This proves vital for maintaining a continuous and consistent crankshaft rotation, always ensuring good performance. Also, it aids in reducing wear and tear on the vehicle’s internal components.
Reduce Stress in the Drivetrain
The car engine flywheel reduces stress in the drivetrain components by stabilizing the engine’s movement and ensuring a steady rotational speed. This helps reduce wear and tear, increasing the durability of universal joints in the driveshafts. Generally, these joints are often in constant rotation to create a seamless transfer from the engine to other parts of the vehicle, like the exhaust manifold and gearbox.
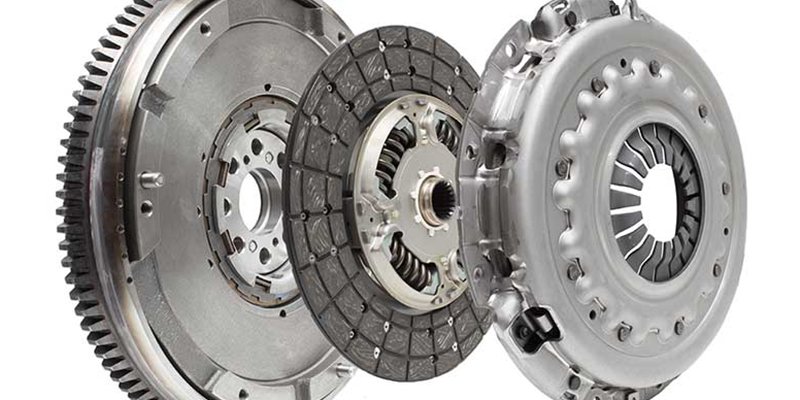 Structure and Components of Automotive Flywheels
Structure and Components of Automotive Flywheels
The flywheel automotive part consists of various smaller components essential for its functions. Below, we will discuss some typical of them.
Flywheel Cover
As the name suggests, the flywheel cover is the structural protective barrier enclosing the entire assembly. It is a sturdy casing that shields this mechanical device from external elements, ensuring it maintains its structural integrity and is durable enough to serve its functions for extended periods.
Outer Rim
The outer rim refers to the automotive flywheel’s peripheral edge, where the mass’s bulk concentrates. It is generally heavier than the internal body, as it contributes to the rotational inertia of the flywheel, enhancing kinetic energy transfer and optimum energy storage. In addition, the rim consists of teeth on its exterior, aiding the engine startup as it interacts with the electric motor.
Mainbody or Disc
The main feature of the flywheel in car engines is the central disc. It is the main component that stores the rotational energy required for the roles of this mechanical device, particularly maintaining the engine’s balance and mass distribution.
Ring Gear
The ring gear refers to the toothed wheel at the outer edge of the flywheel. Its principal function is related to the starting process, where it engages with the pinion gear of the starter motor, causing the flywheel to rotate, followed by the engine cranking.
Mounting Holes
The mounting holes are holes holding a strategic position in the flywheel. They are crucial for securing this mechanical device with bolts and nuts, ensuring it remains attached to the engine’s crankshaft.
Crankshaft Flange
The crankshaft edge is the flywheel area connected to the vehicle’s engine crankshaft. It is typically a machined surface with tapped holes, allowing the use of bolts and nuts to secure it and ensure properly aligned attachment.
Axial and Radial Bearings
The axial and radial bearings are crucial components that support the rotary movement of the flywheel. They aid in compensating for any imbalances in the axial (thrust) and radial forces, enhancing a more balanced and smooth vehicle running. Also, they assist in providing support and effective load distribution, reducing any adverse effects of imbalanced forces.
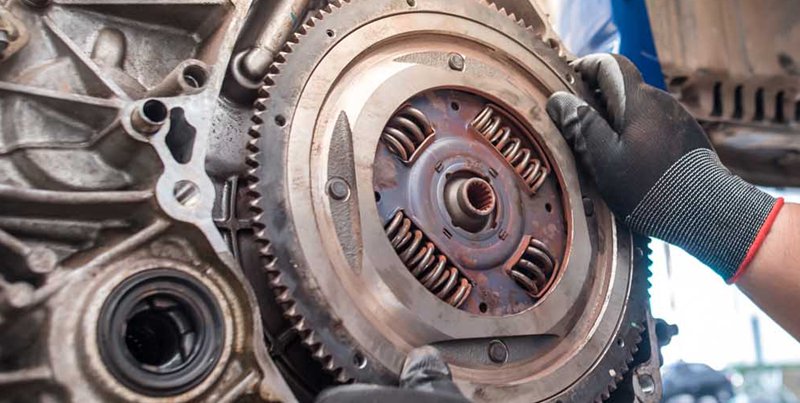 How Do Flywheels Work in Car Engines?
How Do Flywheels Work in Car Engines?
The functioning of a car flywheel is rooted in the fundamental principles of physics and mechanics. At its core, the operational principle is rotational inertia – the same as moment of inertia. This concept is a measure of an object’s resistance to rotation. Therefore, as the engine’s crankshaft rotates, the flywheel’s substantial mass resists changes in rotational speed, ensuring a steady and consistent pace, thereby contributing to overall engine stability.
When gas expansion propels the piston outward during power strokes, the automotive flywheel obtains energy from internal combustion through the crankshaft and stores it as rotational kinetic energy. This stored energy becomes essential during non-power phases of the engine cycle, preventing excessive slowing and maintaining a consistent speed.
In addition, the flywheel reduces torque fluctuations inherent in internal combustion engines. It releases stored energy during non-power phases and maintains constant crankshaft speed, effectively preventing engine stalling. The engagement of the flywheel’s toothed ring with the starter motor initiates the engine rotation and combustion cycle, marking a crucial step in the overall functionality of the automotive flywheel.
Types of Car Flywheels
Car flywheels exist in different forms. This section will explore the different types of flywheels.
Single-Mass Flywheel
As the name indicates, single-mass flywheels have a single-piece construction with no immovable components. It is the go-to automotive flywheel for cost-effective vehicles with a simple design, featuring a straightforward design with little to no complexity. Regardless of their simplicity, they provide quick revving of the automotive engine and aid in maintaining a stable, consistent connection between the engine and the transmission system.
In addition, single-mass flywheels possess significant mechanical resistance to warping and high-temperature conditions, ensuring that they maintain their stability even during sudden speed and gear switching.
 Dual-Mass Flywheel
Dual-Mass Flywheel
Again, the name already gives away the structure of this flywheel. The dual-mass flywheel consists of two masses linked by a damping system. Unlike the former, it is a typical design for newer vehicles, as it enhances vibration and shock reduction, promoting smoother engine running. However, it is more common in cars with manual transmission and diesel engines.
This dual-mass flywheel construction features two pieces – the first attached to the clutch and the other to the crankshaft. It features strong springs and more potent energy storage and transmission capabilities that help to reduce torsional spikes and vibrations, promoting more seamless driving.
Billet Steel Flywheel
Billet flywheels are made from solid steel, ensuring they are strong and highly durable. It is common in more robust vehicles because they are sturdy and reliable. You will tend to find billet steel flywheels in high-performance and super-duty vehicles.
High-Performance Flywheel
As the name suggests, these flywheels are known for their high performance. Therefore, they are the go-to flywheel for racing and high-end vehicles. Manufacturers fabricate them using lightweight but strong materials, ensuring reduced inertia but faster engine response and enhanced acceleration.
Flexplate
The flexplate is not a conventional flywheel. However, it serves the same purpose, especially in vehicles with automatic transmissions. It links the car’s engine to the torque converter and enhances energy transfer.
Sprung Hub Flywheel
This flywheel represents the name, as it features a design that includes a sprung hub or damper that assists in shock absorption. This ensures reduced wearing of the transmission components during clutch engagement. This flywheel is an excellent choice when smooth transient clutch activity is the priority.
 Design Considerations When Customizing Car Flywheels
Design Considerations When Customizing Car Flywheels
When manufacturing car flywheels, there are factors that you need to consider, particularly for custom ones. They are critical for obtaining a delicate balance of performance, reliability, and durability.
Material Selection
Generally, car parts manufacturers use high-strength and durable materials to withstand the vibrations and tensions this mechanical device experiences while the engine runs. However, enhanced responsiveness and driving at higher speeds are prioritized for high-performance and racing vehicles. Therefore, such vehicles may utilize lightweight but strong and robust materials.
Precision And Accuracy
In custom flywheel designs, high precision and accuracy are essential. Therefore, machinists must use manufacturing methods that guarantee these parts’ dimensional accuracy. Consequently, the go-to manufacturing process for such customization is CNC machining, which includes a combo of turning, drilling, and milling operations. These processes ensure the meticulous crafting of these parts, high standards, and the overall efficiency and reliability of the fabricated flywheels.
However, when dealing with bulk-volume production, you may need to consider other methods, such as die casting and stamping. These processes are beneficial, creating high-precision parts, and are cost-effective for large-volume manufacturing.
Surface Treatment Options
Besides selecting the right manufacturing processes and ensuring the precision of these parts, you may also need to employ quality surface treatment options when customizing flywheels. These post-processing options include coatings or suitable heat treatments. They prove effective for reinforcing the flywheels and reinforcing them to thrive in harsh environments that flywheels may be exposed to.
Clutch Compatibility
Ensure that whatever flywheel you select to manufacture for your vehicle perfectly matches its clutch system. Even though you are customizing and improving the vehicle’s flywheel, clutch compatibility is vital. Ensure it integrates seamlessly with the car’s clutch so you can benefit from a seamless driving experience.
 AutoProtoWay: Your Expert Partner for High-quality Custom Automotive Parts
AutoProtoWay: Your Expert Partner for High-quality Custom Automotive Parts
Do you need to manufacture or customize an auto part? AutoProtoWay is a reliable partner for all your custom car parts. We offer services in CNC machining, die casting, injection molding, 3D printing, and various surface treatments, from prototypes to production parts. As a one-stop manufacturer, we ensure all your machined parts suit the desired specifications. We also have an expert engineering team to provide effective machining solutions and affordable prices for your projects. You can confidently start your projects with AutoProtoWay today!
Conclusion
This article provides detailed information about the importance and functionalities of car flywheels. While they exist in different forms, with some variations in performance, they perform similar functions, relating to maintaining a steady speed and improving the driving experience.
FAQs
What material is used in making car flywheels?
OEMs and car manufacturers tend to use sturdy and high-strength materials like cast iron and steel to manufacture car flywheels. These materials possess high density and durability that benefit the functionalities of a typical flywheel.
What manufacturing processes suit flywheel manufacture?
Car flywheels typically require high-precision manufacturing processes. Machinists and OEMs often utilize CNC machining centers to manufacture these prototypes and parts. However, other methods, such as casting and stamping are also effective for large volume production.
What is the difference between a flywheel and a flexplate?
The main distinction between a flywheel and a flexplate is that the latter is standard in vehicles with automatic transmissions, while the latter is typical of manual transmissions. Another difference is that the flywheel is more robust, with the flexplate being thinner. However, they serve similar functions, connecting the transmission system to the car’s engine.




