The car suspension is an integral part of a vehicle. These components make smooth and safe driving possible, particularly during rough terrains or high speeds. The suspension system consists of various structures and components, each with a specific function to improve your comfort when driving.
This article gives a detailed overview of different suspension parts, their function, and the manufacturing methods for making these structures.
What are Car Suspension Parts?
Car suspension parts refer to the system of tires, springs, shock absorbers, and linkages connecting the vehicle to its wheels. This system is essential for the interaction between the tires and the road surface and the eventual movement of the car.
The primary purpose of the car suspension system is to ensure the car tires remain in contact with the road, ensuring proper traction. These features allow for adequate vehicle handling, control, and stability, providing a smooth and comfortable ride for the driver and passengers.
 Functions of Suspension Parts in a Car
Functions of Suspension Parts in a Car
The primary function of the car suspension is to connect the wheels to the car and ensure traction on the roads. However, we can also split its functions into two main points. The first one is shock absorbing, which aids in absorbing the road’s imperfections and improving the quality of the ride.
The other one is to ensure the car remains connected to the road at all times, preventing the effects of external forces from taking the car off the road, regardless of the driving conditions, this refers to the anti-roll or stabilizing effect of the suspension.
Other effects of the car’s suspension include the following:
- Vibration damper;
- Ensure even distribution of car’s weight;
- Enhance braking effect;
- Improve handling and steering response;
- Adaptation to road conditions;
- Improve overall driving experience, promoting comfort.
Components of a Car Suspension
The suspension of a car consists of various components. We have mentioned some of these parts, however, this section will take a more detailed approach to each car suspension component.
 Springs
Springs
The springs function as a shock absorber. Its prominent role is to dissipate energy, dampen, and absorb all the impacts and shocks the wheels experience from the road’s imperfections. In addition, they also can maintain traction on the roads, preventing the effects of friction from transferring to the entire car.
Springs in a car suspension are also crucial for maintaining the standard height of the vehicle, promoting optimum handling and alignment. All these features help in promoting a comfortable drive. Examples of springs in suspensions include the coil springs, torsion bar springs, and the leaf springs.
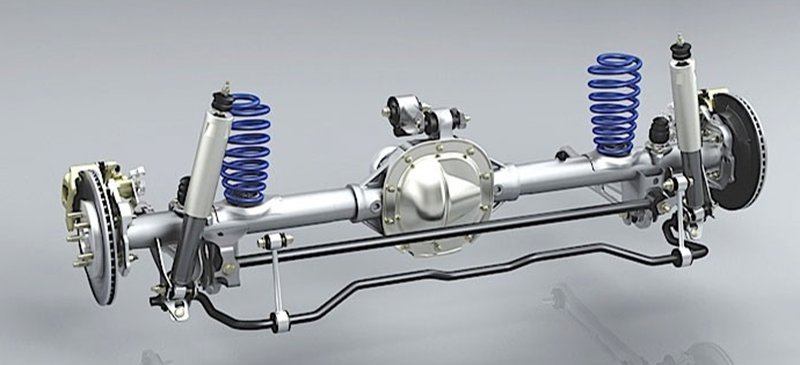 Anti-roll Bar or Stabilizer
Anti-roll Bar or Stabilizer
The anti-roll bar, a stabilizer or anti-sway bar, is another integral component of the car suspension system. As the name suggests, it prevents the vehicle from rolling over, especially when driving on rough terrains or making sharp corners. It aids in stabilizing and maintaining the car’s balance, improving handling, and preventing body roll, especially when making a sharp turn at high speeds.
This bar is typically an iron rod, connecting the lower arms of the left and right wheels and attaching the vehicle itself to the center. These stabilizing rods usually have good elastic properties, which are required to perform their function. At the same time, anti-roll bars transfer energy from one wheel to another, compensating for the centrifugal forces generated during movement through a corner.
Damper or Shock Absorber
The damper or shock absorber’s central role is to dampen and absorb kinetic energy and vibration that results from the vehicle’s motion. You’d agree that the springs perform similar functions. However, the damper helps absorb the energy dissipated from the springs’ oscillatory (up-and-down) movement. They also assist in allowing car tires to maintain consistent contact with the road, promoting stability. Without the shock absorber to absorb the results of the springs’ oscillation, the car bounces, diminishing the driving experience.
 Bumper
Bumper
The bumper is a special component of the car suspension system, it acts as an additional part, consisting of bounding and rebounding. They often offer protective functions for the axle, car frame, and shock absorber.
The car bumpers are usually manufactured using rubber or materials with excellent elastomeric properties to absorb shocks during extreme compression. Typically, they ensure the vehicle’s integrity when the springs expand or contract beyond the maximum limit.
 Lateral Control Rod
Lateral Control Rod
The lateral control rod is another additional component to the car suspension components. However, it is also integral, particularly in four-wheeler vehicles. The main function of this rod is to hold the axle when a load comes from the side.
This rod is usually placed between the vehicle’s axle and the main car body, where it performs its function. In addition, it acts as a horizontal link to other suspension parts, controlling lateral (side-to-side) movement. This lateral sway contributes to the overall stability of the car.
 Knuckle Arm
Knuckle Arm
The knuckle arm is the component of the car suspension at the front of those wheels. It is also called the steering knuckle or spindle, connecting suspension components to the vehicle’s wheel assembly. They allow the car wheels to pivot for steering, contributing to improved handling and the car’s response.
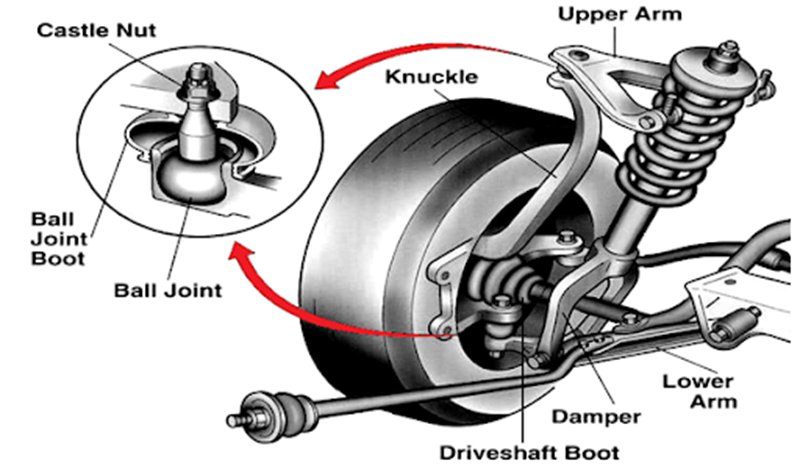 Ball Joint
Ball Joint
The ball joints refer to pivot joints that accept lateral and horizontal loads on the car. It connects other suspension parts to allow for movement in multiple directions. It also serves as a rotation axis when the vehicle turns and contributes to maintaining proper wheel alignment, which is crucial for ensuring even wear.
The car suspension includes the upper and lower ball joints, which function as a unit, aiding the lubrication of the points that run against each other. Therefore, it is important to ensure proper lubrication to ensure the efficiency of this component.
Lower and Upper Arm
The lower and upper arms are components of the suspension system that connect the car chassis and other suspension parts like the knuckle arm, ensuring the wheels remain attached to them. This component functions as the handle moves up and down the suspension system, allowing easy turning of the vehicle and maintaining stability.
Strut Bar
The strut bar helps to hold the lower arm, allowing the front wheel tires to function correctly. Its principal function is to improve steering response and control of the car. Generally, the front wheels act as the deciding factor when turning a vehicle, as they are designed to tilt while the back wheels maintain their position when turning. The strut bar also helps to reduce chassis flex, enhancing overall car rigidity and handling.
Types of Automotive Suspension Systems
Different car suspension systems are available, depending on the vehicle type and specifications. Below, we examine the more common suspension system used today.
 Dependent Suspension System
Dependent Suspension System
The movement of one wheel or component of the suspension system directly affects the other on the same axle. The design of this system is such that it uses a solid rear axle, connecting both wheels. While this suspension system features a simple and cost-effective design, it is not a common choice anymore because it is more common in rear-wheel-drive vehicles.
Independent Suspension System
Unlike the dependent system, the independent suspension system is the go-to design for most modern vehicles, including sophisticated ones. Each wheel connects to a particular spring, solid axle, or shock absorber, allowing independent movement of each wheel minimizing impact on the opposite wheel.
The design of an independent suspension system allows for more precise and accurate alignment of the wheel, promoting better handling, particularly at high driving speeds. However, this system is usually more expensive because of the increased manufacturing complexity.
Semi-Independent Suspension Systems
The semi-independent suspension system consists of elements of the dependent and independent systems. It features a rigid axle with coil springs, connecting the wheels on the same axle. However, like an independent system, each side of the car features distinct shock absorbers.
The semi-independent suspension components of these vehicles are often directly attached to the car frame instead of the chassis. That said, this system displays a good balance of cost and high performance, making them a good choice for compact cars and some SUVs.
Torsion Bars
The torsion bar is a typical suspension design present on the front end of a car, directly linked to the frame. It is a good choice for different vehicle types, including heavy-duty trucks and off-road vehicles. The torsion bar is a long rod featuring a robust and durable spring on either end, allowing energy absorption and distribution. Sometimes, these torsion bars may serve as parts of the spring elements in a suspension system.
Macpherson Struts
This suspension system – Macpherson struts – is named after the inventor John Macpherson, who developed them in 1837 for steam-powered vehicles, particularly trains.
The MacPherson strut integrates a shock absorber and a coil spring into a single unit, simplifying the suspension design. It uses a strut that links to the car body and wheel hub to control the car’s wheel movement. Notably, this system is still in use today, offering structural support in addition to the suspension function. particularly in front-wheel-drive vehicles.
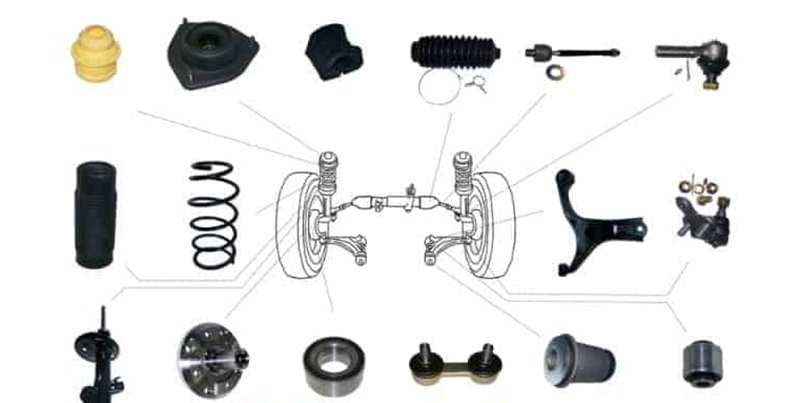 Manufacturing Methods for Car Suspension Parts
Manufacturing Methods for Car Suspension Parts
Various methods are suitable for manufacturing components of a car suspension system. The method selected for each part depends on the compatibility in manufacturing the specific components.
Below, we explore some methods used in the industrial manufacturing of these components.
Metal Casting
Metal casting includes manufacturing processes like sand casting and die casting. The process is suitable for manufacturing suspension components like lateral control and knuckle arms. The metal casting process typically involves heating the specified metal ingots into molten form before pouring them into pre-designed molds featuring the desired component’s shape.
The casting is an old manufacturing process; however, because of its cost-effectiveness, it’s still in use today. Moreover, it retains the structural integrity of the casted parts, even when creating intricate structures that require high precision.
Forging
Forcing refers to the manufacturing method that aids in creating metal parts by reshaping them under high compressional or impact force. It is suitable for creating robust and highly durable components, such as the anti-roll bar, control arms, and specific linkages. The process fabricates parts with enhanced strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance, making it a suitable technique for manufacturing components that experience high stress and loads, such as suspension.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is the go-to manufacturing process for various automotive car parts, including suspension components. The method involves using computer codes to control the movement of machines as they cut through a block of material. The process allows the creation of highly precise parts, making it a popular manufacturing method.
Machining operations, particularly milling, are suitable for fabricating suspension arms, strut bars, and knuckle arms. Even as it creates these parts, maintaining high dimensional accuracy, it maintains tight tolerance specifications and creates them with excellent surface finishing., with less demand for post-processing operations.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is typically used to manufacture non-metallic components, particularly parts of plastics and composites. Therefore, since most car suspension components are made of metals, injection molding these components is not a common choice. However, it is an excellent choice for manufacturing automotive bumpers.
The process involves injecting a molten material, usually plastic or composite, into a pre-made mold cavity where it forms the components’ desired shape. It allows the creation of these bumpers in different sizes, shapes, and design specifications. Also, it is a cost-effective method for fabricating lightweight but high-strengthened parts.
Welding
Welding is a fundamental manufacturing method in assembly and joining two or more metal components together. It may prove effective for joining suspension components to the car frame or chassis or joining one part to another. The process involves heating a tiny portion of the adjoining parts into the molten state to allow the fusing of other parts, creating a strong bond. Welding ensures the integrity and security of the connection, creating a stable and overall high-strength suspension system.
Conclusion
While a car suspension allows the connection of the wheels of a vehicle, it performs a more significant role beyond this. Car suspension components like the springs, shock absorbers, and anti-roll bar are integral for a smooth, jolly ride, preventing the car from bouncing around and absorbing shocks, energies, and imperfections on the roads. They also aid in stabilizing the car, preventing it from rolling over, especially when driving at high speeds.
Are you looking for a reliable manufacturer of custom car parts, contact AutoProtoWay to get started on your projects.
FAQs
What’s the difference between rear and front suspension components?
The design and functionality of the suspension system are the main differences between front and rear suspensions. While the front typically focuses more on steering responsiveness and handling, the rear suspension focuses on stability and weight distribution.
How do springs contribute to the performance of a car’s suspension system?
Springs assist in absorbing and dissipating energy from road imperfections. Along with shock absorbers, they contribute to absorbing shock, promoting a smooth and comfortable ride. They help prevent the car from bouncing around, maintaining proper ride height.




