The chassis of a car is an essential component of any vehicle. It acts as its foundation and point of attachment to other integral car parts. The chassis is often called the vehicle’s backbone, as it determines its structure.
This article explores the car chassis functions, structure, and type of car chassis design. Read ahead for more details!
What is a Car Chassis?
A car chassis is the car’s backbone, the load-bearing component of the car frame, and the point of attachment to other car components, including the frame, suspension, exhaust manifold, steering, wheels, etc. The vehicle’s chassis also serves as the base, providing support and stability to the body, engine, transmission, and other integral components. It helps ensure that various car parts integrate seamlessly, enabling easy movement, turning, and efficient and safe stopping.
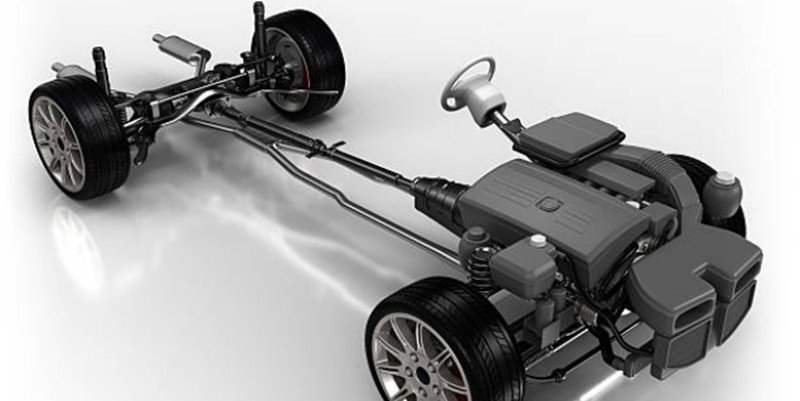 Functions of an Automotive Chassis
Functions of an Automotive Chassis
This section discusses the different functions of the car chassis.
Weight Distribution
The chassis of a car helps spread the car’s weight evenly between the front and rear axles, ensuring balance and handling when driving. It ensures that the vehicle’s weight spreads across all the wheels, providing stability.
Absorb and Distribute Crash Energy
An automotive car chassis also helps absorb and distribute crash energy in a collision or an accident. The chassis absorbs energy through crumple zones and deformation. It then distributes it across the car structure and reduces the effects of the impact forces, causing less risk of damage to the vehicle and its occupants.
Support Different Car Components
The chassis provides a rigid foundation for various car components. It is the attachment point linking various automotive car parts, particularly the steering, suspension, brakes, wheels, engine components, and transmission system. In addition, automotive chassis anchors the brake and clutch components, including the rotors and calipers.
Balance Car Structure
The primary function of the car chassis is to support the vehicle and various components. It supports the engine, drivetrain, and steering system while anchoring suspension, brakes, and clutch.
Other functions of the vehicle chassis include dampening noise, vibrations, and harshness, ensuring a smoother and more comfortable driving experience. In addition, some chassis may feature better handling for improved off-road capabilities.
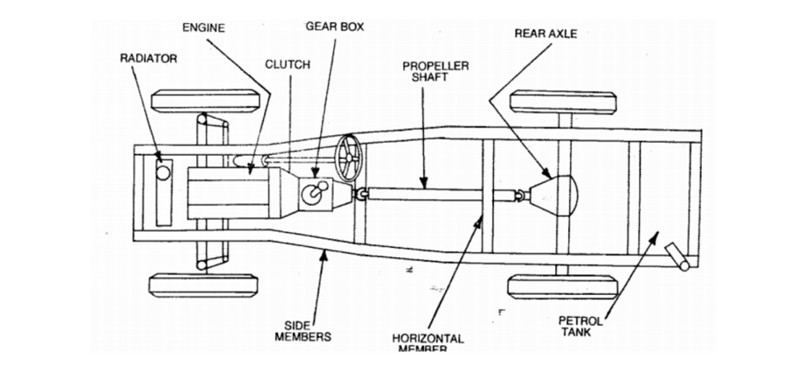 Structure and Components of a Car Chassis
Structure and Components of a Car Chassis
While most chassis of a car feature identical components, there might be some distinction depending on the specific automotive car chassis. This section is about the standard components of a car chassis.
Frame Rails
The frame is the main structural feature of the chassis of a car. It consists of a longitudinal beam made of steel or aluminum, which provides the chassis with its load-bearing capability. They also help support the vehicle.
Suspension System
The vehicle’s suspension system refers to the connections that link the tires, shock absorbers, springs, and linkages to the car’s wheels. The suspension helps maintain stable interaction between the car tires and the road surface. It also helps guarantee smooth handling and easy movement on the roads.
Clutch
The clutch connects and disconnects the engine crankshaft and the transmission. It is essential for smooth gear changing and prevents the engine from stalling during gear shifting.
Rear Axle
The rear axle aids in lower transmission and generates the torque required to power the wheels. It also supports the rear wheels and car suspension parts and enables easy car movement and direction switching.
Braking System
Usually mounted to the car chassis, the braking system works with the suspension and wheel assembly to slow down or stop the vehicle. It uses friction, enabling the conversion of rotational energy in the wheel into heat energy. Most vehicles often feature a disk or drum brake system.
Wheel and Tires
The wheels and car tires are the only components of the chassis that make direct contact with the road. They help the vehicle gain traction on the road, maintain stability and shock absorption, and support it.
Steering System
Like the brakes, the steering system is attached to the chassis and works with the suspension and car wheels to steer and control the car’s direction. It consists of the steering gear and linkage, steering column, and wheel, among other components required to direct the car’s movement.
What’s more, the steering system is generally hydraulic or electric depending on the car’s make.
Cross Member
The cross member refers to the structural components of horizontal beams linking the frame rails, providing extra support and stability. They increase the chassis rigidity and ability to maintain the vehicle’s structure while supporting other components like the engine, transmission mounts, and suspension.
Transmission System
The transmission system directly links to the chassis of a car through the transmission mount. It works in close relationship with the engine and driveline to provide smooth and efficient power delivery.
In addition, the chassis transmission system includes the car gearbox and other components related to gear shifting. The transmission may also help absorb vibrations and noise, promoting a more comfortable ride.
Universal Joint
The universal refers to a flexible coupling connector behind the transmission and the front axle. It connects the transmission to the driveshaft, enabling smooth power transmission. The universal joint also lets the drive shaft rotate at an angle while transferring energy to the wheels.
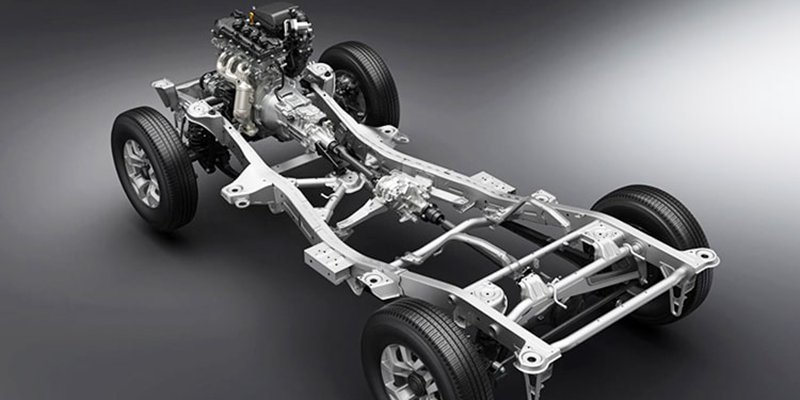 Types of Car Chassis
Types of Car Chassis
You’d agree that not all cars are identical, each presenting a peculiar design. Below, we examine the types of car chassis.
Ladder Frame Chassis
The ladder frame chassis of a car is the conventional car frame design, featuring two parallel frame rails supported by smaller ones. As the name suggests, this car chassis has a unique ladder-like structure. The ladder frame chassis design provides the vehicle with a strong and rigid foundation, supporting the suspension and other integral components of the car chassis.
Pros
- Ladder frame chassis is easy to construct and assemble;
- Provides the car with high structural integrity;
- It is solid and suitable for bulky, load-carrying vehicles like trailers and trucks.
Cons
- The ladder frame chassis is heavy, making it unsuitable for lightweight and high-performance vehicles;
- It exhibits weak torsional ability.
Monocoque Chassis
The monocoque chassis design, also known as the unibody design, fuses the car frame and chassis into a single unit. It is the standard chassis type in most modern vehicles, including sedans, hatchbacks, and SUVs. Therefore, the monocoque chassis design goes beyond aesthetics; it provides exceptional strength, rigidity, and crash resistance.
Pros
- It provides high torsional rigidity;
- The fused design helps to protect its components, making it more durable;
- The monocoque design helps to absorb and effectively distribute crash energy.
Cons
- Because of the fusing with the car frame, monocoque chassis is expensive to manufacture;
- The fused design may make repairs difficult.
 Backbone Chassis
Backbone Chassis
The backbone chassis is sometimes called the central backbone or central tube design, as it resembles the human backbone. This chassis type features a hollow cylindrical tube connecting the front and rear axles and suspension. Due to its high torsional toughness, it is the go-to design for off-road vehicles.
Pros
- High torsional toughness;
- The backbone chassis provides a strong and rigid foundation for the vehicle;
- Excellent for off-road vehicles and passenger cars.
Cons
- It attracts high manufacturing costs
- Issues with the driveshaft may compromise the entire vehicle’s chassis.
Tubular Chassis
Tubular chassis are also known as space car chassis frames, as they consist of a series of networks of tubular members, creating the three-dimensional structure that forms the car chassis. They are common in lightweight, high-performance, and race vehicles. Furthermore, the tubular chassis is the 3D representation of the conventional ladder frame chassis.
Pros
- The tubular chassis offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio and crash resistance;
- Excellent for vehicles with lightweight specifications;
- Allows for enhanced design flexibility and customization.
Cons
- It features a complex design, making construction challenging.
 Manufacturing Processes for Car Chassis Components
Manufacturing Processes for Car Chassis Components
The standard manufacturing processes for making the chassis of a car include the following:
CNC Machining
Custom CNC machining is a precise manufacturing process that uses a computer to control various cutting tools to remove pieces from a material block until the desired shape is achieved. The technique utilizes different operations, including milling, drilling, turning, etc.
This subtractive manufacturing technique is suitable for fabricating parts with complex designs, especially when using multi-axis machines. In addition, CNC machines are compatible with the several materials used in making car chassis: aluminum, steel, magnesium, and composites.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication incorporates different manufacturing processes to fabricate parts and structures using metal sheets. These processes include cutting, welding, bending, forming, stamping, shearing, welding, riveting, etc.
The sheet metal process is versatile and suitable for fabricating various chassis components, including cross members, driveshaft panels, steering components, and suspension control arms. Its main advantage is that it allows the fabrication of parts with increased strength without compromising weight.
Die Casting
Die casting involves heating metal into the molten state before forcing (injecting) it through a pre-made mold, where it solidifies into the desired shape. The technique is already common in the automotive industry, where it helps create chassis components like engine blocks and transmit housing.
Although the manufacturing method has long production cycles, it is a good choice for bulk volume production of car parts. Die casting is suitable for creating components of the chassis of a car, particularly its underbody and suspension links.
Car Chassis Components Finishing Options
Indeed, car chassis are not usually visible, with the body panels being the primary driving force of the vehicle’s aesthetics. However, suitable surface finishing options can enhance the chassis’ mechanical properties and promote durability
Anodizing
Anodizing is a chemical process that coats the surface of a metal with a protective oxide layer. It is often used for aluminum, where the alloy is coated with aluminum oxide. Anodizing the car chassis and its components increases the car’s corrosion resistance, making it more suitable for a corrosive environment.
Painting
Painting is a practical surface finish that involves coating the parts of a chassis with paint. The finish helps to prevent the risk of corrosion of the chassis, frame, and other components. Machinists and OEMs often include other long-term corrosion-resistant substances in the paint to enhance the anti-corrosive properties.
Galvanizing
Galvanization is a surface treatment process that involves applying a zinc coating to the chassis and other parts, like the frame rails. This surface finish ensures the chassis’s resistance to corrosion and abrasions, enhancing its durability and aesthetics.
Polishing
Polishing involves using a high-precision abrasive material to create a smooth and glossy finish on a workpiece. The process can help remove any manufacturing imperfections, enhancing the aesthetics of the chassis of a car. Polishing can also remove minor scratches, pits, and crevices that can accumulate corrosives, improving the corrosion resistance and durability of the chassis components.
 Common Materials for Making Car Chassis Parts
Common Materials for Making Car Chassis Parts
The choice of material for fabricating car chassis requires careful consideration, depending on strength, weight, and cost. Below are the standard materials for fabricating car chassis.
Aluminum
Aluminum is the go-to metal for car chassis because of its favorable properties. It’s a low-density metal with considerable strength, making it suitable for creating high-performance and racing car chassis while maintaining efficient fuel consumption. Since aluminum is lightweight, its alloys have improved mechanical and anti-corrosive properties.
Steel
Because of its superior strength, steel used to be the most common material for creating car chassis. Moreover, it possesses other beneficial features, including easy machinability, durability, cost-effectiveness, and availability. However, steel is less corrosion-resistant and heavy, making it less fuel-efficient and unfavorable for high-performance vehicles.
However, carbon steel is still a common choice in vehicles that require incredible strength. Steel alloys with less carbon content also offer some benefits because of their increased flexibility.
Magnesium Alloys
Like aluminum, magnesium alloys are lightweight, making them an excellent choice for the chassis of high-performance and race cars, particularly when alloyed with aluminum—AZ91D. However, this alloy is less corrosion-resistant than aluminum; therefore, it may require post-finishing to enhance its properties.
Composite
Composites combine various materials, such as carbon fiber, glass fiber, resin, etc. These materials are soon becoming relevant in the automotive industry, including car chassis manufacturing.
These materials are easy to work with and resistant to corrosion and harsh conditions, making them durable. Though expensive, they are lightweight and robust, making them excellent for high-end and race vehicles.
Future Design Trends for Automotive Chassis Systems
Continuous technological advancements are a mainstay in the automotive industry, as car manufacturers constantly look for ways to improve cars. Below, we discuss how modifying a car chassis can help enhance car performance.
Weight Reduction
One of the most common trends in automotive chassis designs is weight reduction. Car manufacturers and OEMs understand the importance of reducing car weight to improve performance and fuel efficiency. As a result, lightweight materials like aluminum and composite are used more often when fabricating the chassis of a car.
Before now, steel was the traditional material for this purpose. However, it is a dense material, discouraging its use, even though it presents excellent mechanical properties.
Enhanced Safety Features
Car designs that showcase enhanced safety features are also gaining traction in future chassis design. These designs utilize innovations such as crumple zones, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and integrated sensors. These technologies improve crashworthiness and occupant protection while enabling features like automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance, and collision avoidance systems.
Integration With Electric Powertrains
The popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates the integration of electric powertrains into chassis design. Newer car chassis must accommodate battery packs, electric motors, and associated electronics while optimizing space and weight distribution. This integration involves modifying the layout of the traditional chassis to lower the center of gravity and improve handling and stability.
Modular Chassis Platforms
Modular car chassis platforms are emerging as a flexible and cost-effective trend in newer automotive design. These platforms allow manufacturers to develop multiple vehicle models from a single chassis architecture, reducing development time and costs. Modular designs allow easy adaptation of different powertrains, including internal combustion engines, hybrids, and electric systems.
WayKen: Your Expert Partner for Automotive Car Parts
Whether you require simple car parts like car lenses, housing, and brackets, or more complex components like the car chassis, light guide, or reflector, WayKen is the partner you can trust.
WayKen offers expertise in automotive part manufacturing, providing high-quality parts that meet your specific needs. With advanced technology and a team of skilled professionals, we ensure precision and reliability in every component produced. Our extensive experience in the automotive industry allows us to deliver parts that meet strict quality standards, from prototyping to production. Choose WayKen as your trusted partner, and experience the difference in quality and service for all your automotive car part needs.
Conclusion
Since the chassis attaches various car parts, it can influence intricate features, such as safety, performance, handling, and fuel efficiency. Therefore, manufacturers and machinists need to understand each design, including other aspects such as material selection, surface finishing, and newer trends, to ensure the creation of an efficient car chassis.
FAQs
Are car frames the same as car chassis?
No, car frames are not the same as car chassis. The frame is the vehicle’s structural foundation, while the chassis of a car includes the fraCme and other essential components like the engine, clutch, transmission, and suspension.
Which car chassis is best for high-performance vehicles?
The monocoque chassis design best suits high-performance vehicles. This chassis type offers superior rigidity, reduced weight, and exceptional handling capabilities.




