What keeps a car moving is the engine, and the heart of the engine is the valve. This essential component regulates the airflow and controls the fuel in the combustion chambers. Not only this, but engine valves also play an important role in expelling exhaust gasses, regulating the entire engine’s performance.
Want to know how these automotive engine valves operate in synchronization with other components? This article discusses everything in detail, from valve mechanism to function and more, so keep on reading!
Two Types of Valves in Car Engine
The two main types of valves are intake and exhaust valves, which control the flow of air and fuel in and out of the engine. Here’s a summary of what they are and how they work.
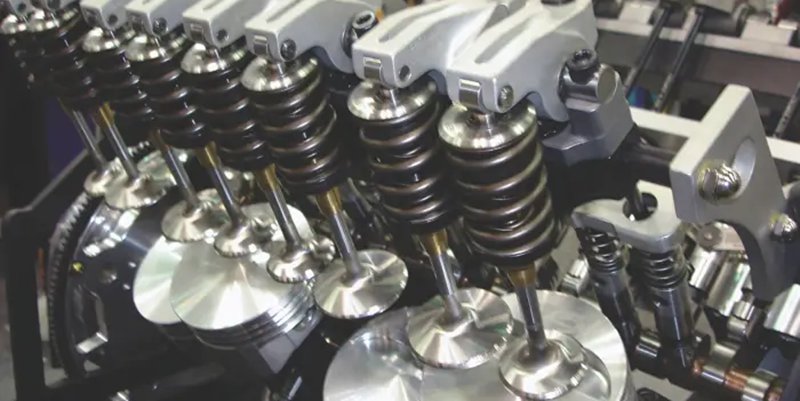 1. Intake Valves
1. Intake Valves
The primary function of intake valves is to let the air and fuel mixture enter the combustion chambers. What happens is that the engine’s piston moves down on the intake stroke, which results in creating a vacuum within the cylinder.
The intake valves open at precisely the right time, immediately allowing the air-fuel mixture in. This precise timing is controlled by the camshaft, which we will discuss below in detail.
2. Exhaust Valves
As its name suggests, the main function of the exhaust valve is to expel exhaust gasses from the combustion chamber. However, a crucial event known as power stroke occurs just between the intake and exhaust stroke, which is important to mention here briefly.
After the air-fuel mixture is injected, the intake valve closes. Then, the piston moves upward, compressing the air-fuel mixture within the cylinder, resulting in the power stroke.
Following this, the exhaust valve opens on the exhaust stroke to force the burned mixture out of the combustion chamber. Like the intake valve, the camshaft also meticulously controls the accurate timing of the exhaust valve.
Main Functions of Valves in the Car
Below are some of the main functions that car valves perform.
Creates Separation
One of the essential functions of engine valves is to create and maintain a seal between the combustion chamber and outside air. This is more important for four-stroke engines as it controls air and fuel intake into the combustion chamber.
However, the cylinder walls tend to be tighter in four-stroke engines, and there’s no intake channel. In this scenario, the valves work as the doors that efficiently separate air from the combustion chamber, helping the engine run efficiently.
Removes Remaining Gas
Once the air-fuel mixture is ignited in the combustion chamber, it produces power that pushes the piston down. When the power stroke occurs, the piston goes back upward, leading to the opening of the exhaust valve. From here, the remaining combustion gasses are expelled to the exhaust manifold.
By opening at the right time, the exhaust valve effectively removes all residual gasses, which makes space for the fresh air-fuel mixture for the next cycle.
Helps in Cooling
As discussed above, the intake and exhaust valves work harmoniously, expelling the hot combustion gasses and letting in the fresh air. This process maintains the continuous and steady airflow into the combustion chamber, keeping the engine cool and running efficiently.
 Aids in Noise Reduction
Aids in Noise Reduction
Thanks to the camshaft, the intake and exhaust valves open smoothly at the right time. This precision prevents any pressure abruption and maintains the air-fuel mixture’s perfect flow. In addition, the accurate closing of valves also dampens the sound waves produced during the combustion process, leading to a smooth and noiseless engine performance.
Prevents Backflow
The valves fit perfectly and tightly against their seats to form a strong barrier that prevents gasses from escaping or re-entering the combustion chamber. At the same time, the camshaft takes care of the timing and controls the opening and closing of the valve. This synchronization is the key to preventing any unwanted backflow.
Different Components of Automotive Engine Valves
Ever wonder how car valves work with utter precision? It’s because they are manufactured with extra care of structure and quality. Here are the main components of car valves.
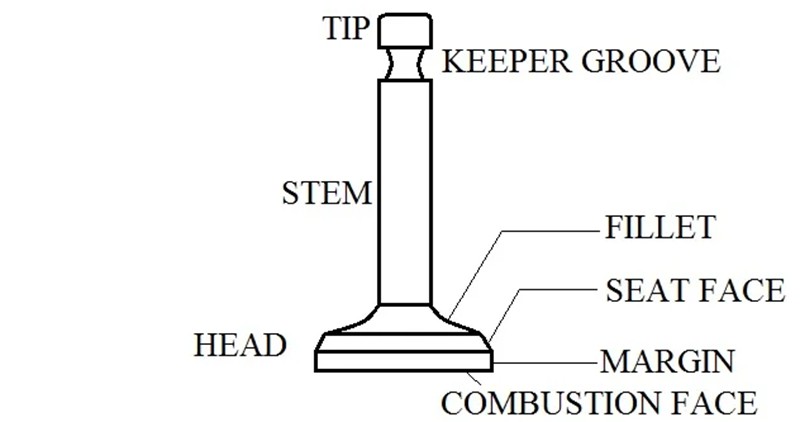 1. Valve Head
1. Valve Head
The flat circular part of the valve is called the valve head. The main function of this particular component is to seal the valve seat in order to control the flow of gasses in the combustion chamber.
2. Valve Face
The angled surface of the valve head that comes in contact with the valve seat is known as the valve face. The angled design is thoughtfully manufactured to help achieve a proper seal to prevent any air-fuel leakage during the process.
3. Valve Seat
It’s the part of the cylinder head where the valve face rests upon closing the valve. This component is essential for creating a gas-tight seal and is manufactured using a combination of wear-resistant and high-thermal-conductivity material.
4. Valve Spring
The primary purpose of valve springs is to close the valve after the camshaft opens it. It also keeps the valve closed during the power stroke and compression. Hence, it is the most stressed part of a valve.
5. Valve Guides
Valve guides are cylindrical components that control the up-and-down movement of the valve in a straight line. They not only help with the valve’s alignment but also minimize the wear on the valve stem. They are made with cast iron, sintered steel, bronze, and other wear-proof materials.
6. Valve Lifters
Valve lifters, also known as tappets, are cylindrical components that sit on the camshaft and transmit the motion of the cam lobe to the rockers and pushrods to open and close the valves. There are two types of lifters: hydraulic lifters and solid lifters.
The main difference is that hydraulic lifters adjust automatically to maintain zero valve clearance, whereas solid lifters need manual adjustments and more maintenance.
7. Valve Keeper
Valve keepers or valve retainers are responsible for locking the valve spring into the valve stem. They are manufactured to keep the valve spring in place during the engine’s operation.
How Do Car Valves Work?
As mentioned above, valves in the car engine are responsible for controlling the flow of air-fuel mixture into the cylinder and letting the remaining gasses out of the combustion chamber. Below is more of a detailed explanation of how car valves work.
 The engine valve’s mechanism is achieved through the camshaft, which is itself driven by a crankshaft. When the camshaft rotates, the lobes control the opening and closing of the valves according to the engine’s timing.
The engine valve’s mechanism is achieved through the camshaft, which is itself driven by a crankshaft. When the camshaft rotates, the lobes control the opening and closing of the valves according to the engine’s timing.- When the piston moves downward, the intake valves open up and create a vacuum in the cylinder. This particular action lets the air-fuel mixture into the combustion chamber from the intake manifold.
- Once the intake valves are closed after the intake stroke, the piston moves upward, leading to the compression stroke. This stroke compresses the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, and then the spark plug ignites the compression mixture to initiate the power stroke.
- After the power stroke, the piston moves upward again, and the exhaust valves open. This allows the remaining burnt gasses to vent out of the cylinder and pass into the exhaust manifold.
What Materials Are Suitable for Making Car Valves?
There are two basic types of steel used to manufacture car engine valves: martensitic steel and austenitic steel.
Martensitic Steel
Martensitic steel is magnetic in nature, and steel alloys with a martensitic grain structure have a high hardness at room temperature (35 to 55 HRC) after tampering. This capability of martensitic steel enhances its strength and resistance. All these characteristics make it one of the best steel choices for producing engine valves.
However, martensitic steel loses its hardness at extreme temperatures, like 500°C and above. This steel is mostly used for intake valves, which typically run around 400°C to 500°C.
Austenitic Steel
This steel type is non-magnetic and softer than martensitic steel; hence, heat treatment cannot harden it. In some cases, to improve the wear resistance, a hardened wafer is welded on the tip of the valve stem. For instance, an austenitic stainless valve head is welded to a martensitic stem, which creates a two-piece valve with a long-wearing stem and a high-resistant head.
Automotive Valves Manufacturing Processes
The raw material undergoes several steps before taking the final finished shape as the engine valve. Here are the machining processes that a valve goes through.
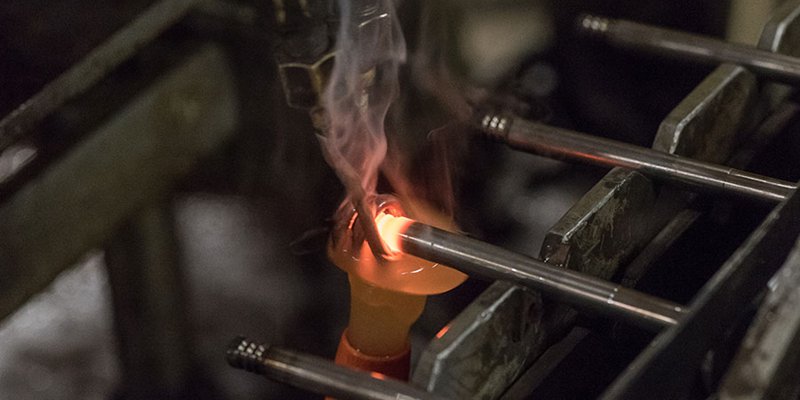 1. Cutting or Extrusion
1. Cutting or Extrusion
The raw material arrives in the form of bars, which are cut to length until the desired diameter of the bar is achieved.
2. Welding
The friction welding process is required to join the metal bars in scenarios where the valve head and stem are supposed to be made using different materials.
3. Upsetting
After the above processes, the raw material is further dented to provide the initial shape required for the forging stage. Upsetting compresses the billet between two dies, consequently reducing the height of a part while increasing its diameter.
4. Forging
The upset portion is immediately forwarded for the forging, during which the metal is heated and molded using compressive force. This process is the key point for refining grain structure and improving the mechanical properties of the valve.
5. Heat Treatment
This process involves three steps: quenching, washing, and tempering. Quenching reduces the crystallinity of metal, whereas tampering minimizes its brittleness.
 6. Surface Treatment
6. Surface Treatment
This step involves shot blasting, which employs high-velocity steel abrasives. During this step, the surface of the valve is cleaned and further treated for secondary finishing procedures.
7. Surface Finishing
This is the concluding machining process of automotive valves, which is done to get the final desired shape of the valve. The surface finishing is done by hard chrome plating, which enhances the valve’s wear resistance and eventually increases its lifespan by providing a durable surface layer.
What are the Common Valve Problems and Their Consequences?
The wear and tear of parts of a valve in the engine is a common issue that occurs for various reasons. Below are some typical valve problems and consequences it may cause to the working of the engine.
Incorrect Valve Clearance Setting
This particular issue occurs when the valve clearance is set too tight, or there has been a long interval between the maintenance checks. As a result of this problem, the valve does not close properly, and combustion gasses may also flow from the valve seat, eventually heating the valve head.
Installation of Valve Springs Error
This issue may occur if the spring is not inserted correctly during the installation process. The ill-fitted spring may cause a lateral bending moment on the valve stem. The bending stress results in a fractured valve stem and may even destroy the valve guide.
Faulty Installation of Hydraulic Tappets
The minimum waiting time required after installing the tappets is 30 minutes. If this timing is not observed, the excess oil in the tappet doesn’t get the time to escape completely. This premature engine operation may cause the valves to strike against the piston, eventually causing it to break or bend.
Misalignment at the Valve Seat Insert or Valve Guide
If the valve seats or guides are non-centric or misaligned, the valves will fail to close properly, and consequently, they will overheat or burn through in the seating area.
 Contact Autoprotoway for High-standard Custom Car Parts
Contact Autoprotoway for High-standard Custom Car Parts
If you are looking for professional services for prototyping or custom machining car parts, AutoProtoWay can help you achieve your manufacturing goals with precision. We have 20+ years of industry experience and 60+ highly skilled experts who can handle a wide range of projects, from prototypes to part production. Our advanced facilities are equipped with different technology to ensure every part meets the high standards of quality and performance. Whether you need components for classic car restoration or innovative parts for automotive product development, AutoProtoWay delivers exceptional results on time and within budget.
Conclusion
Valves in the car engine are the components that regulate the entire combustion of the vehicle. Hence, it is important to understand their functioning and timing for optimizing the engine’s fuel efficiency and power output.
FAQs
What damages the engine car valves?
Burnt or damaged valves can be caused by various factors. One of the most common factors is leaking seals and guides and other compression problems. When those issues co-occur with the cooling system or exhaust gas recirculation malfunctions, the valves get burned.
What’s the average cost of repairing a car valve?
Commonly, the cost of repairing of automotive engine valve ranges between $240 to $330. This cost is largely attributed to labor cost, which usually ranges between $200 to $300, whereas the parts’ cost is much lower i.e. around $26 to $58.
What’s the average lifespan of valves in the car engine?
There’s no definite lifespan for an engine valve. Any engine valve will wear out once the vehicle has been driven for long enough. However, if the components are made of premium-quality material, they will definitely last longer. As an estimate, if the valves belong to a drag racing engine, it may endure around 150,000 miles.




